Toe Problems
Don’t Let Toe Problems Slow You Down
Foot pain and discomfort can significantly impact your quality of life. Whether you’re dealing with bunions, fungal nails, hammertoes, ingrown toenails, or arthritis in your big toe, seeking proper care and treatment is essential. Our experienced team is committed to providing accurate information and compassionate support to help you understand your condition and find effective solutions for pain relief and improved mobility. We prioritize your well-being and strive to empower you to make informed decisions about your foot health.
Bunions
 Bunions are a common toe problem. A bunion is a bump on the inside border of the foot at the base of the big toe. The big toe commonly angles towards the second toe and the foot become wider.
Bunions are a common toe problem. A bunion is a bump on the inside border of the foot at the base of the big toe. The big toe commonly angles towards the second toe and the foot become wider.
Bunions are usually caused by factors such as genetics, wearing tight or narrow shoes, or having certain foot deformities. Over time, the pressure and friction on the joint cause it to become swollen, painful, and inflamed.
Common symptoms of bunions include pain, redness, swelling, and stiffness around the affected area. The big toe may also angle towards the other toes, causing crowding and discomfort. Bunions can make it difficult to find comfortable footwear and can interfere with normal activities.
Treatment for bunions focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing the progression of the condition. This may involve wearing wider and more comfortable shoes, using protective pads or cushions to reduce pressure on the bunion, applying ice to alleviate swelling, and taking over-the-counter pain medications. In severe cases, a healthcare professional may recommend custom orthotics, splints, or bunion surgery to realign the joint.
It is important to note that bunions are progressive and can worsen over time if not properly managed. If you are experiencing persistent pain or difficulty with everyday activities due to a bunion, it is advisable to seek medical advice for proper evaluation and appropriate treatment options.
Fungal Nails
Fungal nails, also known as onychomycosis, are a common 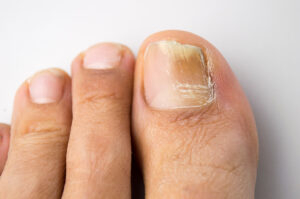 toe problem characterized by a fungal infection of the nails. It typically affects the toenails but can also occur in the fingernails.
toe problem characterized by a fungal infection of the nails. It typically affects the toenails but can also occur in the fingernails.
Fungal nails occur when fungi, such as dermatophytes or yeast, invade the nails, leading to an infection. Factors such as warm and moist environments, poor foot hygiene, damaged nails, or weakened immune systems can increase the risk of developing fungal nails.
Signs of fungal nails include thickened nails, yellow or brown discoloration, brittle or crumbly texture, and distorted nail shape. The nails may also become separated from the nail bed, causing pain or discomfort.
Treatment for fungal nails usually involves antifungal medications. Topical antifungal creams or solutions can be applied directly to the affected nails, while oral antifungal medications may be prescribed for more severe or persistent infections. In some cases, a healthcare professional may recommend a combination of both treatments.
Preventing fungal nails involves practicing good foot hygiene, keeping the feet clean and dry, wearing breathable shoes and moisture-wicking socks, avoiding walking barefoot in public places, and regularly inspecting the nails for any signs of infection.
It is important to address fungal nail infections promptly, as they can be persistent and may spread to other nails or individuals. If you suspect you have fungal nails or have concerns about your nail health, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Hammertoes
Hammertoes are one of the most common toe problems. Hammertoes are a foot deformity where one or more toes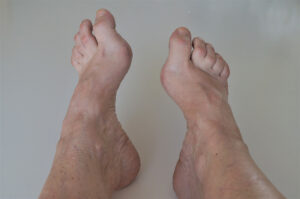 bend or curl downward instead of pointing straight. The affected toes resemble a hammer or a claw.
bend or curl downward instead of pointing straight. The affected toes resemble a hammer or a claw.
Hammertoes can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, wearing tight or ill-fitting shoes, foot structure abnormalities, or muscle imbalances. Over time, the tendons and ligaments in the toes become imbalanced, leading to the abnormal bending or curling.
Common symptoms of hammertoes include pain, discomfort, corns or calluses on the top of the affected toes, difficulty in finding comfortable footwear, and limited flexibility or movement of the toes.
Treatment for hammertoes depends on the severity of the condition. Mild cases can often be managed with non-surgical measures, such as wearing roomier and more supportive shoes, using orthotic inserts or pads to alleviate pressure, practicing toe-stretching exercises, and managing corns or calluses with appropriate care.
In more severe cases, when the deformity causes persistent pain or interferes with daily activities, medical intervention may be necessary. This can include corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation, splinting or taping the toes to realign them, or, in extreme cases, surgical correction to straighten the affected toes.
If you suspect you have hammertoes or are experiencing foot pain and discomfort, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and guidance on appropriate treatment options.
Ingrown Nails
Ingrown nails are a painful, common toe problem. Ingrown nails occur when the edge of a toenail grows into the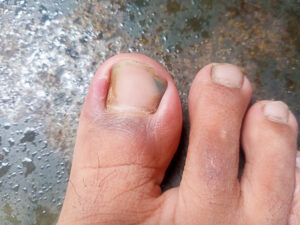 surrounding skin instead of growing straight. This can lead to pain, redness, swelling, and possible infection.
surrounding skin instead of growing straight. This can lead to pain, redness, swelling, and possible infection.
Ingrown nails commonly affect the big toe but can occur on any toe. They can be caused by improper nail trimming, tight shoes, trauma to the toe, or genetic factors.
Symptoms of an ingrown nail include pain along the edge of the nail, tenderness, redness, swelling, and possible drainage of pus if an infection develops.
Treatment for mild cases of ingrown nails may involve soaking the foot in warm water, gently lifting the edge of the ingrown nail, and placing a small piece of cotton or dental floss under the nail to encourage proper growth. Wearing comfortable shoes with room for the toes to move can also help.
In more severe or recurrent cases, medical intervention may be necessary. This can involve trimming or removing the ingrown portion of the nail, applying a chemical to prevent regrowth, or, in some cases, surgical removal of a portion or the entire nail.
Prevention of ingrown nails involves proper nail care, including cutting nails straight across and avoiding tight-fitting shoes. Keeping the feet clean and dry can also help prevent infections.
If you have an ingrown nail that is causing significant pain, shows signs of infection, or does not improve with home care, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment.
Stiff or Arthritic Big Toe
Stiff or arthritic big toes refer to a condition where the joint at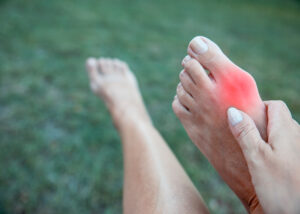 the base of the big toe becomes stiff, painful, and less flexible. It is a common toe problem caused by arthritis, which is the inflammation and degeneration of the joint.
the base of the big toe becomes stiff, painful, and less flexible. It is a common toe problem caused by arthritis, which is the inflammation and degeneration of the joint.
Arthritis in the big toe can be a result of wear and tear over time, injury, or certain medical conditions. It leads to the breakdown of cartilage and the formation of bone spurs, causing pain, swelling, and limited range of motion.
Symptoms of stiff or arthritic big toes include pain, stiffness, swelling, tenderness, difficulty bending or straightening the toe, and a feeling of grating or grinding within the joint.
Treatment options for stiff or arthritic big toes aim to relieve pain, improve mobility, and manage the underlying arthritis. This may include medications for pain and inflammation, physical therapy exercises to improve flexibility and strength, using assistive devices such as splints or orthotics for support, and making lifestyle modifications like wearing supportive footwear and maintaining a healthy weight.
In severe cases where conservative measures do not provide sufficient relief, surgical intervention may be considered. This can involve joint fusion or joint replacement surgery to alleviate pain and improve function.
If you are experiencing persistent pain or stiffness in your big toe, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options tailored to your specific situation.